Concept of recession-proof
Firms plan to be resistant to downturns and remain stable during extreme financial times. To do this, they utilize a few procedures. In the first place, they enhance their items or administration so they’re not excessively subject to one area of business. This implies assuming one piece of their business dials back, others can in any case get cash. Second, they work on making their activities more productive, which assists them with reducing expenses and setting aside cash. Third, they develop monetary reserve funds to have a pad on the off chance that deals drop. Additionally, they place a strong emphasis on offering essential goods and services that people require even in times of recession. Firms are better able to deal with economic downturns, keep their operations running smoothly, and be well-positioned to rebound when the economy picks up.
Abstract
The purpose of this article is to improve comprehension of the connection between entrepreneurship and economic recession. The course of business, instead of the actual activity, is a, and such intricacy surfaces when neighborhood setting conditions demolish after a financial downturn. The methods and strategies that businesses can use to avoid a recession are examined in this paper. The outcomes show that business ventures recoil during monetary slumps, recommending a favorable pattern to repeat. A more vulnerable discernment by people of the valuable open doors coming about because of the shake-out makes sense of, generally, the lower inclination to make firms during a monetary downturn. The GDP growth chart, which is driven by the components, consumption, and business investment, is the most important tool for highlighting the significance of financial resilience, operational flexibility, and market adaptability. Businesses may be able to select from the relatively deeper pool of unemployed labor, significantly improving the quality of their staff, and it is crucial for recession-proofing in a company.
A resilient business can withstand downturns.
As organizations detailed their profit from the subsequent quarter, it was obvious that changing buyer ways of behaving are harming results, particularly among customer confronting areas. What comes straightaway?
Firm flexibility is essential since associations that improve are prepared to endure startling disturbances and recuperate from them rapidly, bringing about a scope of advantages, including:
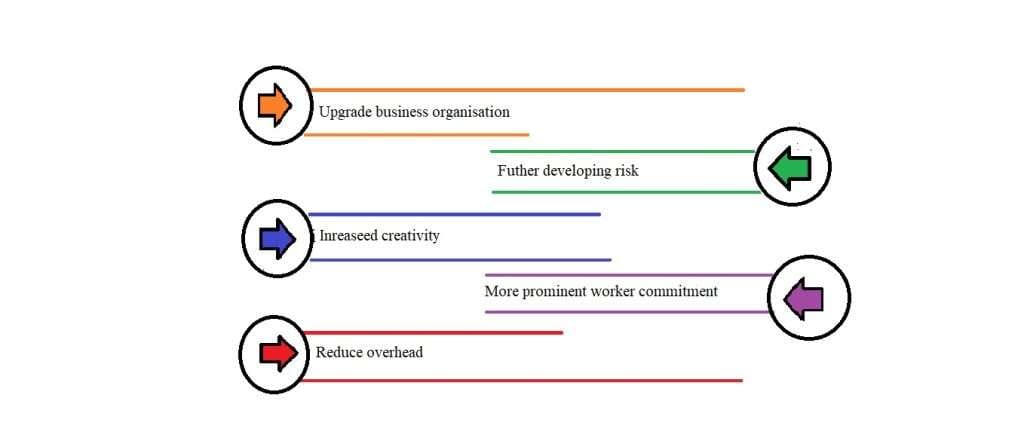
- Upgraded business progression: Companies can minimize the impact of disruptive events on their operations by developing organizational resilience. They are able to continue delivering products or services to customers, protect revenue streams, and reduce downtime as a result.
- Further developing the risk: Organizations can reduce the likelihood of business disruptions and the costs associated with them by using resilience strategies to identify and mitigate potential risks before they escalate into crises.
- Increased creativity: Versatile Associations are bound to explore different avenues regarding new plans of action, items, or administrations, as they are sufficiently spry to adjust to startling difficulties and open doors. This implies more hours spent on growing new items or improving items that as of now exist, rather than time lost to take a chance with moderation.
- More prominent worker commitment: A versatile association cultivates a culture of readiness, trust, and straightforwardness, which can further develop worker confidence, inspiration, and maintenance.
- Reduce overhead: Above costs are costs that stay consistent while paying little attention to income, so they become especially dangerous in a downturn. Yet, a slice-and-consume approach can hurt more than great, so recognizing three phases of the above decreases: simple managing, cuts that require cycle changes, and exceptional cuts is useful. Simple management could incorporate reconsidering contracts with providers or changing sellers for administrations like office cleaning or media communications, or lessening or killing staff advantages. The next step might be to reduce spending on travel and entertainment and outsource certain tasks, both of which would require alterations to the workflow. Extreme above decreases are those that can yield the most investment funds; however, they are the most problematic. More drastic cuts include eliminating employees, consolidating real estate, and transitioning to a remote workforce.
Conclusion
When business pioneers know they’re in a downturn, many might feel it’s past the time to do much else significant than cut costs. Downturn sealing a business should start some time before the monetary slump shows up. To avoid potential errors, which are more likely to occur when managers are ill-prepared for a crisis, recession-proofing should be approached carefully and thoughtfully. It requires an equilibrium of careful expense cutting, brilliant client showcasing and vital speculation.

